Designing Effective Moderation Tools: Essential but Often Overlooked Aspects of Public Digital Spaces
Student Projects
While exploring PubHubs’ potential for public organizations, UX design student Laura Mostert identified moderation tools as a critical yet underdeveloped component for maintaining healthy civic discourse in digital environments. This aspect of her design work deserves special attention given its importance for sustainable online communities.
Key Insights from Experienced Moderators
Micky van Zeijl
This article explores the moderation features of Laura Mostert’s PubHubs design, created as part of her Minor UX Design project at Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences. Link to her Figma prototype
As a moderator herself, Mostert brought firsthand experience to her research, supplemented by in-depth interviews with experienced community moderators whose insights directly shaped her design decisions. Safety emerged as the paramount concern during Mostert’s research. Moderators shared stories of facing significant challenges, including doxing attempts, which led Mostert to establish moderator safety and anonymity protection as a foundational design principle.
Her research revealed that content assessment is more nuanced than automated systems can handle. While AI helps flag potential issues, it struggles with contextual understanding and sarcasm detection. Effective moderation tools must complement rather than replace human judgment. Moderators emphasized the need to leave notes on rule-breakers and track behavior patterns over time. This insight drove Mostert to incorporate robust user history and notation features in her design.
Communication between moderators proved essential for maintaining consistent standards. Moderators reported using platforms like Slack or Messenger to discuss challenging cases and align their approaches, which inspired Mostert to integrate communication features directly into her moderation tools.
Comprehensive Moderation System
Based on her research, Mostert developed a moderation system with distinct components designed to address real-world challenges faced by community moderators.
The core of her design features a dedicated moderation panel accessible from the left menu. Here, moderators can view user-reported content awaiting review, examine automatically flagged content based on keyword detection, manage blocked keywords, and customize content filtering options based on their community’s specific needs.
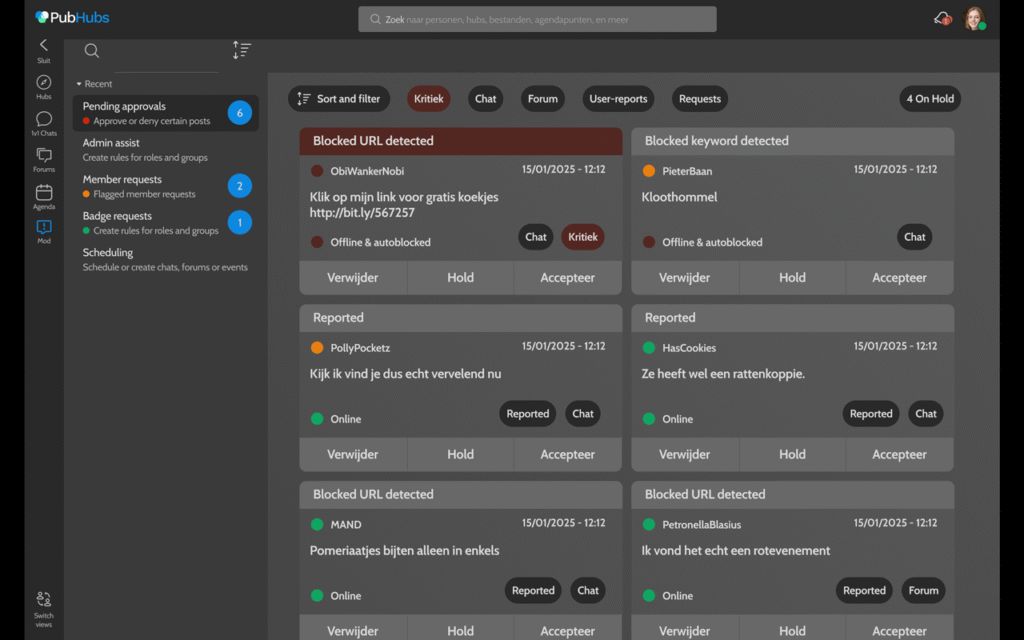
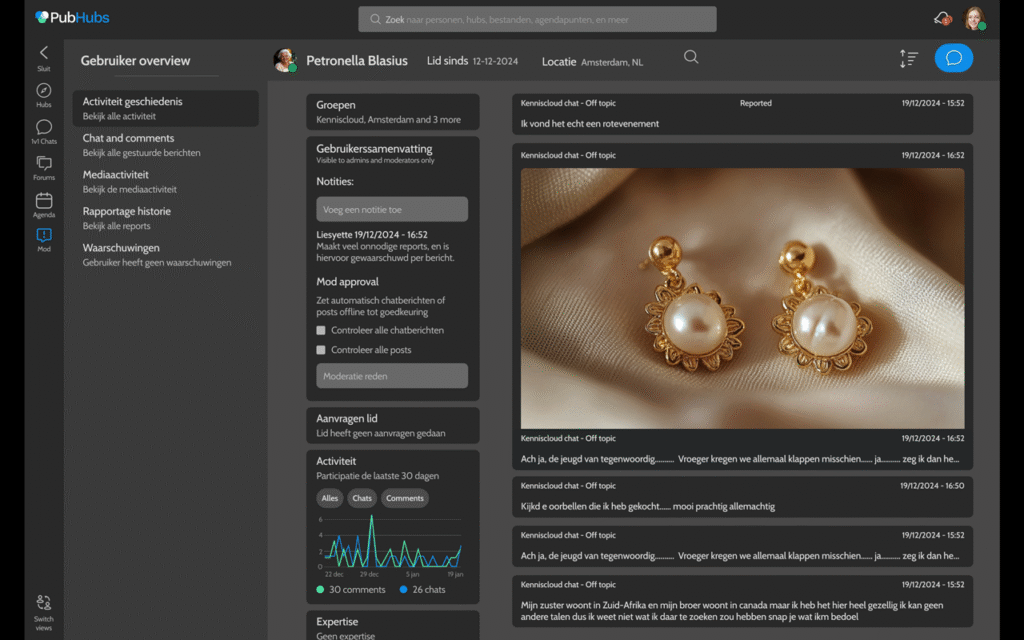
Mostert balanced effective moderation with privacy protection through thoughtfully designed user management tools. Moderators can toggle post-approval requirements for users with previous violations, attach private notes about concerning behavior patterns, and access high-level location data that helps identify potential threats without revealing specific personal information. Comprehensive user history reviews allow moderators to identify patterns rather than reacting to isolated incidents.
For swift intervention when needed, Mostert integrated immediate message removal options directly within chat interfaces and added user muting capabilities accessible during live conversations. She deliberately placed more serious actions, such as banning or kicking users, within user profiles to encourage moderators to consider these measures carefully before implementation.
Prevention forms a key element of Mostert’s approach. Her design includes forum category management tools and permission setting adjustments that help shape positive interactions before problems arise. Content organization capabilities maintain clarity and focus in discussions, reducing the likelihood of misunderstandings that can lead to conflict.
Balancing Visibility with Safety
“I want it to be clear that someone is a moderator so you can easily search for them and ask them questions,” explains Mostert in her documentation. This philosophy guided her approach to moderator visibility.
Her design establishes clear moderator labels in public discussions, making authority figures easily identifiable to community members seeking assistance. Accessible moderator profiles improve the experience for those needing help. Simultaneously, the system protects moderators’ personal information to prevent harassment—addressing a serious concern highlighted in Mostert’s interviews.
All of these moderation tools integrate seamlessly into the platform, remaining invisible to regular users while providing powerful capabilities to those maintaining community standards. This approach maintains the natural flow of community interaction without creating an atmosphere of surveillance.
Design Recommendations for Civic Platforms
Mostert’s work offers valuable recommendations for civic digital spaces seeking to implement effective moderation. Digital platforms should prioritize moderator safety by designing systems that protect the individuals maintaining community standards, recognizing the potential for harassment and ensuring appropriate safeguards.
Moderation tools should offer graduated response options, supporting interventions ranging from gentle corrections to account restrictions. This flexibility allows moderators to respond proportionally to different situations, preserving community relationships whenever possible.
Team coordination features are essential for maintaining consistent standards. Mostert emphasizes the importance of communication tools that allow moderator teams to share insights, discuss challenging cases, and develop collective wisdom. Finding the right balance between authority and protection remains crucial—community members should easily identify moderators while moderators’ personal information remains secure.
Finally, Mostert recommends designing structural elements that reduce the need for active moderation in the first place. Thoughtful architecture of discussion spaces can naturally encourage constructive interactions, improving the experience for both community members and moderators.
Impact on Civic Digital Spaces
Mostert’s moderation design for PubHubs demonstrates how thoughtful UX can support healthier online civic engagement. By creating tools that balance authority with safety and transparency with protection, her work establishes a framework for digital civic spaces that can effectively self-govern while remaining open and accessible.
Her design proves that moderation tools need not be intimidating or intrusive—they can be naturally integrated into the user experience, becoming an extension of the platform that supports rather than hinders community interaction. This approach allows public institutions to create online spaces that reflect their civic values and foster meaningful dialogue among community members.